This Is Why Lean Software Development Is Amazing

Lean production principles are widely employed in different industries. They are also applicable to software development.
Using these principles leads to optimized programming efforts, budgeting, and lower defect rates. Optimizations can be up to 33%.
Many organizations can benefit from Lean development principles. They eliminate extensive pre-planned specifications.
User stories form the basis for the software development process. These are easier to understand than long lists of specifications.
Making something that no one wants or likes is a waste of time and money. Lean manufacturing focuses on providing quality and value for clients and production teams.
This article will first discuss the history of Lean development. Then it will show how to apply it and why it is so good for companies of any size and makeup.
Applying these principles is not straightforward; it requires a change in thinking. This guide also explains what the concepts of value, wanted, and others mean in the setting of Lean software development.
What is Lean Software Development
In general, Lean development is a management framework. It helps to optimize the use of time and resources.
This eliminates waste and delivers the product in its most essential form.
The basis of the Lean philosophy is an iterative cycle of trial and error. Some have summarized it as: “fail early to succeed sooner.”
Innovation is at the core of developing digital products. Yet, failure is a healthy element of a software development process as well.
Another expression used in this connection is Minimum Viable Product, or MVP, strategy.
A development team markets a minimalistic version of their products. Then they use user feedback to learn what is good about the product or what consumers would like to see added.
Agile or Lean principles are very similar. They both focus on the people in the team, rather than on the tools that the project uses.
They both give the people a lot of power and freedom to act and make unified decisions.
But there are also some differences. Lean focuses on the optimization of workflows.
It does this by monitoring the amount of work that a process requires. It aims to eliminate any part of the process that does not add value.
On the other hand, Agile principles break down tasks and organize them into sprints. It focuses on small amounts of work that are then executed quickly and efficiently.
Even though there may be parts of the sprints that have no direct value, they are not eliminated. The focus is more on delivering the working product.
The History of Lean Software Development
To understand how lean software development started, think back to the middle of the last century.
The Japanese car manufacturer Toyota was experiencing problems with its product delivery. They noticed that the manufacturing processes were too long.
Hence, the company was not able to deliver its products on time. They understood that they needed a different project management system.
The Lean manufacturing principle finds its origin in car production. If you know about Toyota, this isn’t news to you. If you don’t, you can check out this video:
Yet the same principles are equally applicable to other fields.
It also works in fields like banking, engineering, product development, and supply chain. It has only recently that these principles found application in software development.
After the publication of the Agile Manifesto, developers began to take an interest in other approaches to their work. The Lean philosophy found use in software development around 2003.
What interested the Lean development pioneers was the focus on the complete organization. The introduction and final achievement of Lean projects are by iterative cycles.
Every cycle, developers remove anything that does not add value to their product. That helps to constantly test and check the product and detect bugs.
What are the Strengths of Lean Software Development?
The introduction of the Lean software development methodology does more than streamline teamwork. It has benefits for the entire organization.
It improves cost-efficiency, productivity, and profit. This is the result of the combination of well-defined principles and work practices.
Lean principles focus on making products that exactly fulfill the needs of customers. It prevents a development team from making features that no one wants.
To do this, it obtains information straight from the source, the customer.
A Lean development strategy consists of short iterations. This gives the team a chance to work with a small set of plans to start with.
Then, in small iterative cycles, the developers make needed adjustments and anticipate situations. Thus, they have the power to work fast and put improvements in place in a flexible way.
This provides major advantages in decision-making.
Lean and Agile software development methods make organizations reconsider their quality control systems. That in turn changes the way they deal with release readiness.
Quality monitoring is not only a job for higher management. Rather, it becomes part of everyday communication between members of the developing team.
Finally, the focus of Lean software development is positive. It looks in the first place at adding value, not at eliminating costs.
We can help you turn your idea into reality, take over your existing project, or extend your current development team.
Schedule a free consultation at hello@tms-outsource.com, or fill out the form and we will follow up with you shortly.
Lean Software Development’s Strengths
It Eliminates Wasteful Losses
Lean software development aims at delivering essential features.
Once the minimal viable product is on the market, the development team can learn what to improve. They can also see how to prioritize this work.
Customer input is vital in this stage. Unproductive work and investments are thus prevented.
It Generates Innovative Solutions
A Lean software development team will want to add value and invest time in innovating. Innovation is at the core of present-day advancement.
It Shortens the Development Cycles
The advantages of shorter production times are obvious. The team can deliver more in a shorter amount of time.
That allows an organization to deliver more projects, which benefits the finance department. It also helps to keep customers satisfied.
Rationalizes and simplifies the development process
Lean software development principles help make the development process simpler. It eliminates unnecessary stages.
That makes it more focus-oriented, faster, and cheaper. It saves on the most important resources, money, and time.
Increases the team involvement rate
A Lean development team is much more involved. This is because it puts a large part of the decision-making in their hands.
Employees that feel empowered form a more motivated team. The value of this cannot be overstated.
Lean principles eliminate micromanagement and the forced execution of decisions. Both are demotivating management techniques.
Motivated team members with decision-making powers deliver higher quality end products.
It Reduces Redevelopment of the Product
Having to redevelop because a product was not made right in the first place, is inefficient.
Lean Management Tools

- Inventory management.
This reduces the number of operations. It involves the application of constraint and queuing theories.
- Kanban
Kanban is a workflow management system of Japanese origin. Its goal is to prevent the simultaneous completion of different process stages.
This is to prevent the overloading of other process stages.
- Value stream mapping.
This is a method to visualize an entire software development lifecycle. It starts with the client’s request and ends with the deployment stage.
It helps to understand and optimize the amount of time spent on things like processing and downtime.
Seven Lean Principles of Software Development
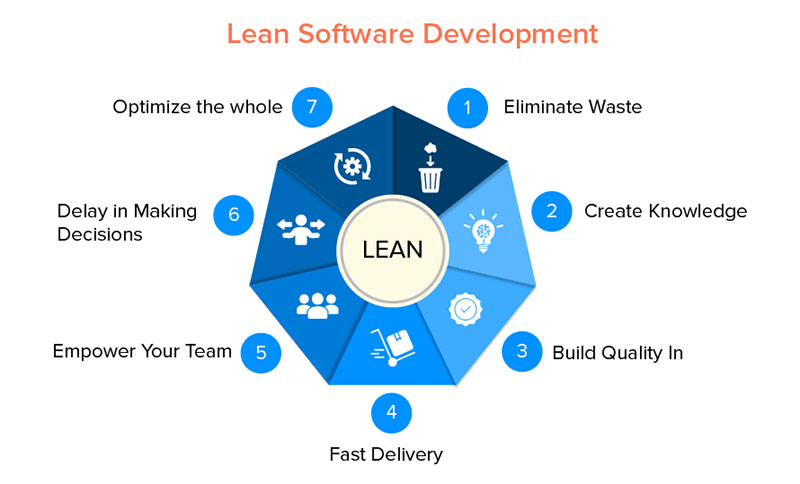
The next section is based on Mary and Tom Poppendieck’s book “Lean Software Development: An Agile Toolkit”. This shows the effective application of lean principles to the development of software.
Below is a summary of the principles.
Eliminate Waste
The elimination of waste is an indirect focus of the Lean methodology. The production of waste takes away value from the product that the client receives.
In this context, waste can refer to activities like rebuilding code or testing code. Or doing any activity more than once.
This may sound innocent but it bears a variety of quality issues. Lean means being more efficient.
According to the methodology, it’s vital to eliminate anything that does not add value. More specifically, this refers to defects, partial work, idle time, and unnecessary features.
This reduction is the first principle of Lean software development. It defines the entire philosophy.
Below is a list of types of waste that it tries to get rid of.
- Data duplication
- Engineering process delays
- Communication inefficiency
- Quality issues
- Tasks overload in log
- Unnecessary code and features
- Unneeded and stifling bureaucracy
- Unclear requirements
- Costs associated with the aforementioned
Build In Quality
A second guiding principle in any Lean development process is quality management. Poor quality management leads to different kinds of waste, as discussed above.
All development teams want to build quality into their work. Yet, quality is not always expressed in the product.
Consistent quality is only possible if this is part of disciplined practice. Often, attempts to make a quality product lead to waste in excessive testing.
A first step in building quality is free communication between the team and the client. This helps the development team to make the product the client wants.
A second one is to think about how to eliminate anything that creates waste. For example, make it a practice to immediately fix bugs, instead of making a long backlog.
Avoid task switching, test code immediately, and create automation. That keeps the quality of the product as high as possible throughout the development process.
In the Lean approach, team members build and integrate all the time. Continuous integration reveals if all parts are working and working together well.
That keeps each part of the development phase productive.
Create Knowledge
Lean software development has its roots in Lean manufacturing. In manufacturing, Lean deals with simplification and standardization of production lines.
So, it was necessary to generate knowledge of the process and make unusual changes. The Lean concept comes with the “amplify learning” concept.
This concept proved to be a game-changer.
As teams move through projects, they gain a deeper understanding of what a client needs. They also learn what the limitations of their products are.
The code that developers produce is usually not Lean from the beginning. They will find errors and bugs and then try to improve the code.
This is part of the learning process of developers. They gain knowledge by solving problems and making variations on their initial code.
This teaches an important lesson.
In Lean software development, improving existing code and building on it is the best approach. It generates more understanding than detailed planning and documentation.
Decide as Late as Possible
Managing a project requires a balance in planning. Planning is necessary, but a long rigid list of tasks and dates is counterproductive.
Planning is not the same as making a commitment.
Software development has many uncertainties. Making late decisions allows for making better-informed decisions.
With time, more information becomes available. Hence, delaying a big decision is the best way to go.
Late decision-making is something to build into a project.
The Lean methodology aims to produce flexible software so that it is easy to add or change features. That is something to consider for after the release of the product.
But it emphasizes that software projects contain a high degree of uncertainty.
The next point may come as somewhat of a surprise. Late decision-making saves money.
This is due to the fact that it helps to shorten development times.
Looking for a development partner?
If you’re looking for a technology partner, development team augmentation, or just a company for your software&app development initiatives, consider TMS.
TMS is a software and digital company in Belgrade, Serbia. We develop innovative and modern software.
A few examples include premium booking software Trafft, MedTech apps like MR Prepare, or MarTech/AdTech apps like the Advise Media Suite, among other great software examples.
Check out our services and also some of the work we’ve done for our clients. Who knows, maybe we’ll form a successful relationship.
Schedule a free consultation at hello@tms-outsource.com, or fill out the form and we will follow up with you shortly.
Deliver Fast
A happy customer is more likely to stay than one who has to wait for their product. Fast delivery also saves time for the developing agency.
Short development cycles are also beneficial in terms of the learning curve. Developers learn much more from the feedback they receive.
It allows clients time to think about final details, like design. Again, this helps to eliminate waste in both learning and communicating.
Of course, everybody wants to deliver their work as fast as possible. So, what is preventing them?
These are some common time consumers:
- Slow communication
- Over-engineering solutions
- Thinking too far ahead
Respect for People

Development teams need general plans and reasonable goals. With that, they should know how to work based on empowerment and self-direction.
They are very skilled people and well able to use their heads to solve problems.
Helping developers to develop independent thinking skills is part of the Lean approach. People that work and think autonomously can make very good decisions.
This philosophy is part of the Agile and Lean development methodology. Encourage independence and respect in the following ways:
- Proactive and effective communication
- Empower others to give their best
- Encourage healthy conflict
- Tackle any work-related issue as a team
Optimize the Whole
Lean software development does not leave room for narrow-mindedness. At best, optimizations will be local, not company-wide.
A small picture approach will hamper the growth of the company and will push it into a small niche in the market. Instead, think broad and long-term.
The perception of the user and the software’s characteristics must coincide. If that is the case, the customer will enjoy working with it and perceive the system as reliable.
Conceptual integrity means that the components of a software solution work well together. The total product is better than the sum of all components.
There will be a balance between efficiency, flexibility, responsiveness, and maintainability.
Ending thoughts on lean software development
Everybody is looking for better efficiency in the workplace. Achieving this often requires a change of mindset to improve work practices.
It also requires the right methodology. Many companies find the Lean software development approach works well for them.
It helps to streamline processes. It forces teams to cut out anything that does not contribute to the value of the product.
Another key element of this approach is to keep the software developers at the center. They are the ones that will deliver the quality product.
To summarize, these are the core principles of the Lean approach:
- Continuous improvement
- Respect for people
- Continuously experimenting, failing, and trying again
- Currently, Lean is the best management solution for the tech industry. It’s all about speed.
Mistakes are fixable in subsequent iterations.
Pay attention to what the end-user thinks about the product. That helps the development team to come up with fresh ideas.
If you enjoyed reading this article on lean software development, you should check out this one about software development outsourcing trends.
We also wrote about a few related subjects like offshore software development, lean software development principles, how to hire a web development team, software development budget, business pivot examples, financial projections for startups, financial software development companies, IT outsourcing failures, and risk management processes.

