How To Protect an App Idea – Don’t Get Your Work Stolen

The developers of Flappy Birds game made the headlines when The Guardian found out that nearly one-third of all games released on the App Store within the 24-hour period were Flappy Bird clones.
What’s even more shocking is that 4 of the top 5 free iPhone games in the U.S. App store are Flappy Bird clones.
They weren’t the only ones who were affected though. Nearly 97 percent of all top Google Play Apps and 87 percent of App Store Apps were copied in the last few years. Among them are also popular consumer apps such as Uber.
Consequences are obvious – these clones can seriously harm your business and steal potential app users. All of this can lead to decreased revenue and market share loss.
There are a few effective measures that you can take during the app development process to protect your app idea from the competitors and to minimize risks. In this post, we’ll try to present the most important ones.
The Most Common Types of App Protection
There are a couple of different types of legal protection you can get for a mobile app. Some are more expensive than others but here’s a simple overview of each type of protection and who should consider getting them;
Protect Intellectual and Physical Assets of the App with Copyright
A copyright is a form of protection provided to the authors of ‘original works of authorship’. These include the literary, dramatic, artistic, and certain types of intellectual works, both published and unpublished.
Copyright is an obvious choice for protecting source code, in-app copy, and graphic design that goes with it. Getting a copyright registration is typically a fast and inexpensive process. Here, you can learn more about how the process works. If your company is based in the US, you’ll want to check the US Copyright Office. Usually, everything is done for less than $1000.
Although Apple and Google have great security procedures, someone can still jailbreak a phone to extract the source code from an app. Even worse, they could tweak a few lines of code and launch it as their own app. That’s why copyright registration is one of the most important types of protection.
It gives you a legal resource if someone tries to attempt something like this. However, note that copyright registration doesn’t protect the idea of the app. It only covers the intellectual and physical assets of the app.
Exclude Others from Making, Using, or Selling with a Patent
A patent is typically given for an invention. It is the grant of a property right to the inventor. In the US, it is issued by the United States Patent and Trademark Office. This gives inventors the right to exclude others from making, using, or selling the specific invention in certain territories where the inventor holds the patent.
Patents hold more power because its requirements are much more stringent. They protect original ideas from other businesses that are highly unlikely to come up with these ideas and inventions by themselves.
In order to be granted a patent, your idea and all the steps that brought that idea to fruition must be completely original. Patents are also way more expensive than copyrights – they can cost between $8k-$15k.
Mobile apps can be patented because their components are the methods of interaction; for example, the process running on a mobile phone that connects to a remote server containing data. However, the code that runs the software cannot be patented, it can only be copyrighted.
So, should you patent your mobile app? Here are a couple of things to consider.
First, you should check the U.S. Patent & Trademark Office (USPTO) to see if your app would be eligible for a patent. The USPTO will look closely whether your mobile app has ever been patented or published before.
Since it takes time to develop an invention, many mobile app developers will choose to file a provisional patent application first, which is the standard utility patent application in order to secure a filing date.
This one is less expensive than a non-provisional utility patent application.
This provisional application will require a detailed description of the invention, including additional material such as drawings, flow charts, and illustrations of how the app works.
Some owners and mobile app developers will opt to distribute their apps through open-source licenses, whether or not they have received a patent.
However, without a patent, the developer won’t have control over what apps are distributed via open-source licensing. This means that your code could easily be stolen by another developer without giving you any type of credit.
Protect Your App’s Name With a Trademark
Most brands focus on protecting the technology of the app but they completely overlook the importance of protecting its name too. The protection of the app’s name is what’s known as trademark registration.
In the mobile app world, a trademark is used to prevent others from using the same name as yours, but it won’t prevent others from creating a similar app under a different name.
The best time for companies to trademark their name is as soon as the downloads start growing. Filing a trademark early on is an easy and straightforward process. It typically costs less than $200.
Before settling on a name, most brands can check if their desired name is available on their country’s respective Patent and Trademark Office. Consulting a trademark attorney on this journey is also recommended.
After this process is done, the next most important step is reserving it on the app store, registering your domain name, and creating social media accounts.
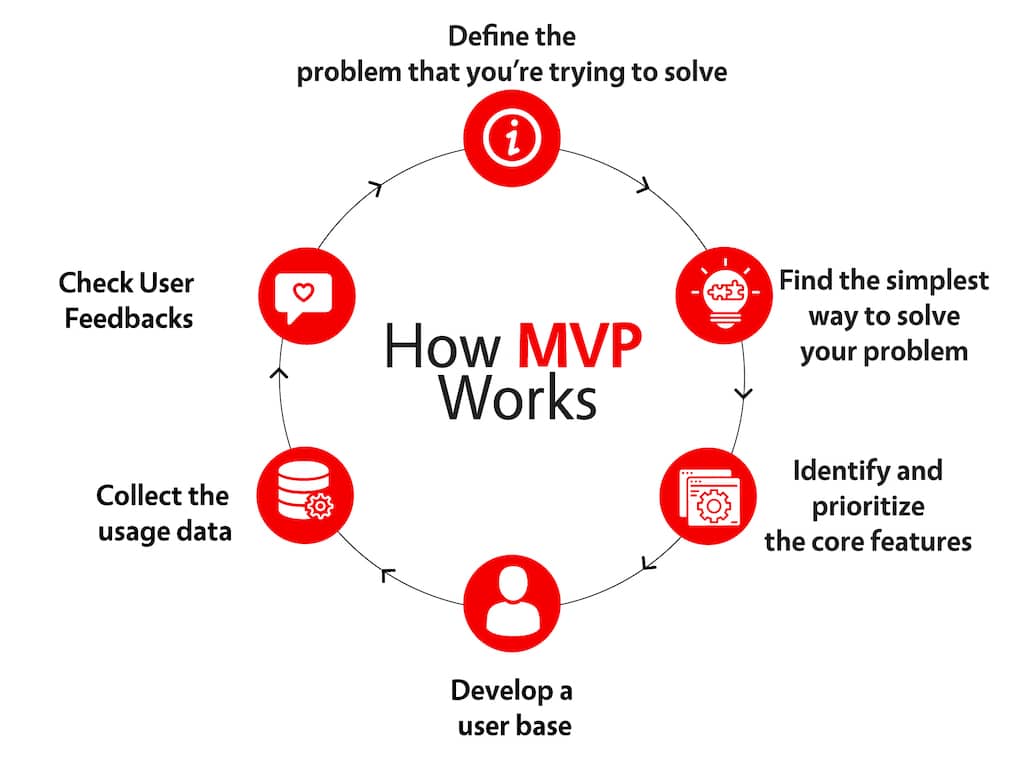
MVP
In ideal circumstances, the start of the project should begin with the release of the minimum viable product.
In addition to being effective from the point of view of implementing a successful project, MVP also provides protection for your idea and project. Once an MVP is publicly available, your idea is protected by copyright as the first published.
An MVP also gives you an advantage in the market. Here are 8 steps to mastering MVP in app development process.
Source: RedBytes
Set up Google Alerts Notifications
A good practice is to set up Google Alerts notifications for the keywords and the name of your project so you can react in a timely manner if the copies of your product appear online.
Specific Steps for Protecting an App Idea
1. Selectively Share Information
The simplest way to protect your app idea is to be selective with who you share important information with.
Sure, explaining your app idea will be necessary in some cases, when pitching to clients and in some other instances but you don’t need to go into more details than necessary.
It’s no brainer – the less you reveal your product, the less likely it is for someone to steal it. Many app creators make this mistake by sharing their idea with whoever will listen.
2. Work With Trustworthy Partners
Unless you plan on creating your new app by your in-house team, you’ll need to outsource its development and design to an external agency. That’s why it’s extremely important to work with reputable individuals and companies.
Before doing so, make sure to screen all third-parties carefully. Go through their website, read testimonials, and check their past clients. Good agencies should have portfolios and case studies listed on their websites.
A third-party developer or designer owns the code once the app is created. A crucial thing is to have a contract beforehand that expresses all copyrights of the app are to be released to you once the project is completed.
3. Draft NDA Agreements
An NDA, a Non-Disclosure agreement, is a simple way to ensure that all shared information will stay confidential between two parties. Whether it’s outsourced contractors, associates, consultants, potential clients or investors, an NDA will provide an added layer of protection. You can get a free template of an NDA agreement here.
However, NDAs don’t guarantee that your idea will be 100 percent safe. It’s still very important to do good research on reputable companies you’ll be working with.
Some investors may be hesitant to sign an NDA, so a good rule of thumb is to include a confidentiality agreement within your business plan that is given to potential investors.
4. Use The Non-Compete Agreement
This agreement is typically used internally to keep employees from revealing your app idea and sensitive information to rival companies. It also stops anyone who currently works on your project to work on any other project that could be a direct competition to yours.
However, non-compete agreements need to be reasonable as they can significantly limit contractors from accepting future projects even after they have finished working with you. The contractor is more likely to sign the agreement if it has a reasonable time frame.
Constructing a non-compete agreement should be done with a lawyer.
5. Invest In Security
The security of your app also starts from the development stage. A well-planned architecture of the app will prevent any hijacking. If your mobile app is built in accordance with all modern security approaches you can be sure that no one will steal your code.
After putting so much effort into designing and maintaining a great app, the last thing you want is a security breach that could derail users’ trust.
Here are some common steps to improving your app’s security;
Review Your App’s Login Page
The login page you use to access your app’s administrative page should be disguised into something less obvious than the typical URL (”www.mysite.com/login”, for example). Once a hacker finds your login page all they have to do is guess the password.
By changing your default URL login page you’re adding an additional layer of difficulty that will discourage hackers. Try a URL that includes random characters, remove links to the login page from your site, and even limit sharing the login URL beyond employees who really need the access.
Secure Your App’s Input Fields
If your app has places for users to leave comments, send messages, and input text, hackers may use that to attempt to inject damaging code.
Such attacks could allow hackers to manipulate and even delete a database, gather email addresses to use in phishing attacks, access financial and private information and more.
There are a couple of ways to guard your input fields against hackers. First of all, you can implement form validation. This is code built into your app and it helps prevent the app from accepting malicious scripts. This validation will automatically differentiate between a harmless comment posted by a user and malicious commands that could hurt your business.
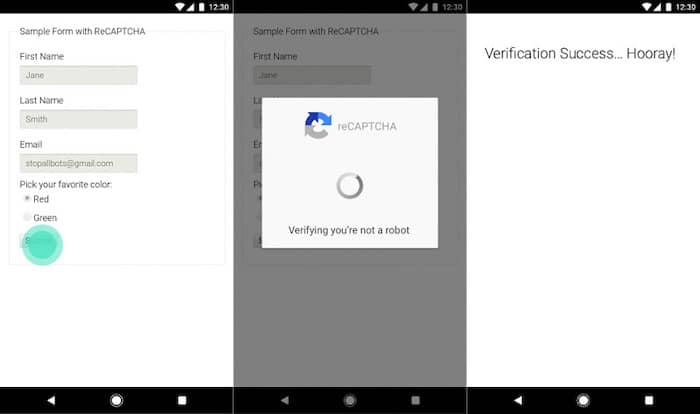
A popular tool to use in this case is CAPTCHA which can appear in several variations. Users are typically asked to check a box signifying that they are human users or to identify parts of a photo.
CAPTCHA is less common on apps but it can be a helpful tool for apps that are also accessible in browsers.
Source: Fonearena
Implement Encryption
No matter where you store your users’ information, encryption is a strong security option.
Encryption serves to translate your data into a code that looks like gibberish at first glance. Even if hackers manage to intercept that data they wouldn’t be able to immediately understand it. Meanwhile, the original form is being sent to the right users.
The most common data encryption algorithms are known as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). It’s also considered to be among the safest ones. It’s used by the US Federal Government and almost all Android and iOS applications run this encryption method.
Other industry tested algorithms include RSA (2048 bits and higher), TDES (minimum double-length keys), ECC (160 bits and higher).
You can also checkout our guide on How to develop a secure Fintech app.
6. Document Everything
Everything that you do with your app needs to be put in writing. Save all the documentation related to it, no matter how small it may be. This will be extremely beneficial, for any technical due diligence or if any legal troubles arise.
You should document your app’s code, brainstorming sessions, meetings conducted with consultants, the final drafts, etc. Not even small details that are relevant to your app should go amiss.
A good rule of thumb is to keep a log of each and every discussion that you had with anyone related to the app. This will be useful if you find out that the information from these very conversations has leaked.
7. Secure Domain and Social Media Names
Securing domain and social media names are another important tool in your security arsenal. Buying a domain name at an earlier time than a competitor’s registered trademark could solve many issues in the case of disputes.
Just note that buying .com extension won’t be enough. In order to protect your domain name from copycats, you’ll want to buy other common extensions from a domain registration service such as .net, .co, and others. There are more than 280 domain extensions worldwide and here you can see the most common ones.
It’s also a good idea to check the social media channels you plan to use and reserves usernames for each one of them.
How To Protect An App When Developing With an Agency
If you decide to work with an agency always ask them to sign an NDA.
Every professional mobile app development agency will already have these documents and will gladly sign upon request. Mutual NDA’s will keep all information you share private and will secure that everything after the completion will remain yours.
Signing an NDA is just one layer of protection but it still won’t guarantee that your app will be 100 percent safe. The best way to protect your app during the development stage is to work with a reputable company.
Conduct thorough research and make sure that your agency has quality reviews and a list of satisfied clients.
How To Protect Source Code
As already explained, one of the best ways to protect the app’s source code is by signing an NDA with everyone included in the process.
A good way to manage and protect data is with the use of DLP (Data Leak Prevention) tool.
One of the most famous ones is McAfee Total Protection but there are many other DLPs on the market such as Symantec DLP, Forcepoint DLP, Digital Guardian Endpoint DLP, SecureTrust DLP, etc.
Still, no DLP can give a 100 percent warranty that no leakage will occur. There’s also a DLD (Data Leak Detection) tool that tracks any launch of your code and notifies you immediately.
Another straightforward way that prevents source code from getting out into the world is by simply restricting which team members have access to it. Institute 2-factor authentication to ensure that no suspicious characters find their way into your source code.
Do You Need Help Protecting Your App Idea?
Here at TMS Outsource, we have a wealth of experience in planning, building, and enhancing top-notch web applications. We are happy to answer your questions, including working with you on protecting an app idea and making it come to fruition.
Feel free to schedule a free consultation and see what we can do together.
