The Software Development Methodologies You Could Use

Development team managers often seek to add structure to the project workflow. For successful project management, choosing a software development methodology is vital.
The chosen methodology will enable smooth development according to the project requirements.
All methodologies have strengths and limitations and work differently in different situations. To handle specific software development projects, teams need the right software development methodology.
However, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all methodology for every development team.
Here is an overview of the most utilized and recognized software development methodologies. This information will help managers to decide which is right for their team.
What Is Software Development Methodology?
The methodology for a software development life cycle is actually a structure.
Teams use it to plan and control the procedure of creating a specialized information system. This enables them to achieve the desired goals.
It can be used by massive organizations with large teams working on projects. Or by a single freelance developer.
Application development defines the process of how the application is made. It generally follows a standard methodology.
With this methodology, the software development process does not involve any technical aspects. But it does demand proper planning for the software development lifecycle.
Getting the best out of one depends on the team structure, requirements, and goals. It’s also possible to use different software development methodologies for different projects.
Waterfall Development Method

Image source: ukessays.com
Many view this as the traditional method of explaining the software development process.
It clarifies the process into a linear flow with a specified sequence. Users see that levels are progressive and depend on the completion of the previous one.
This application development method is like a waterfall because once you go down, you can’t go back up. Everything flows downward.
The development team works together over a set period of time. Their goal is to build exactly what the specifications outline.
Typically, they must finish one stage before beginning the next. This can help with organization and assignments.
Knowing the full scope of the project in advance makes it easy to measure software progress.
Application
The waterfall method is often used by plan-driven teams who have a very good view of the nature of the project. However, development teams who do not work in a gap can also find good outcomes with the Waterfall model.
Pros
- The linearity makes it easy to understand, particularly for new developers.
- It is easy to manage projects because of the rigidity of the model. Moreover, each phase has specific deliverables and an individual review process.
- All specifications and deliverables are spelled out before the development commences.
- This model saves a significant amount of time, with all phases processed and completed at a given time.
Cons
- The waterfall development method is often slow and costly. This is due to its rigid structure and tight controls.
- There is no possibility to develop working software until the last stage of the cycle.
- It doesn’t include customer feedback in the early phases. This increases the risk of the project veering off target.
- Testing is only executed at the end of the development. Some problems are harder to fix at a later stage.
Agile Development Methodology
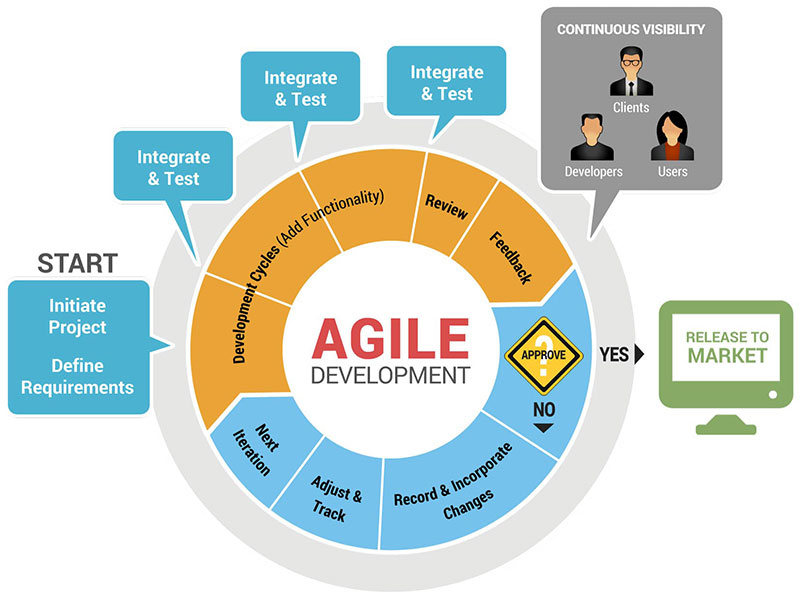
Image source: cyberhoot.com
Teams use the agile development methodology to minimize risk. Risks include such things as bugs, cost overruns, and changing requirements.
This is especially vital when adding new functionality.
In all agile methods, teams develop the software in iterations. Each iteration contains mini-increments of the new functionality.
Agile separates work into distinct phases called sprints. Each sprint lasts a few weeks, during which team members pursue a list of deliverables.
The agile development team members and the Scrum master check the task as the sprint ends.
Agile values individuals and their relationships and interactions more than tools. It features customer collaboration throughout the development process.
It responds to change instead of following a set-in-stone plan. It also focuses on presenting working software rather than documentation.
Application
Agile project management methodology is also more team or squad-based.
RAD involves working directly with a programmer. With Agile, the application development team includes testers, UX designers, technical writers, and many others.
Some may need a framework for development that can help to deal with the volatile marketplace dominated by consumers. They should definitely consider implementing the philosophy of Agile software development.
The Agile methodology is ideal for projects with fast-changing requirements.
Those building software in a new niche will want to use Agile. It works best to implement the additional ideas as one learns more about the market needs.
Pros
- It minimizes peril by creating software in short time boxes, known as iterations. These can last from one week to one month.
- Clarity between team members during development, thanks to the frequent and transparent development.
- Changes in project requirements are easy to address and work on with little impact on the timeline.
- Customer satisfaction by rapid, continuous delivery of useful software.
- People and interactions are key, rather than processes and tools. Customers, developers, and testers have constant interaction with each other.
- Agile methodology has an adaptive approach. It enables users to respond to the changing requirements of the clients.
Cons
- Those used to the waterfall method may have difficulty adjusting to an agile SDLC.
- The team can sometimes lose focus due to overwhelming change requests.
- Documentation takes a back seat in Agile, which can be a problem later on in development.
- At the start of the software development life cycle, it is hard to assess the effort needed. This is the case with some software deliverables, especially the large ones.
Feature-Driven Development Methodology
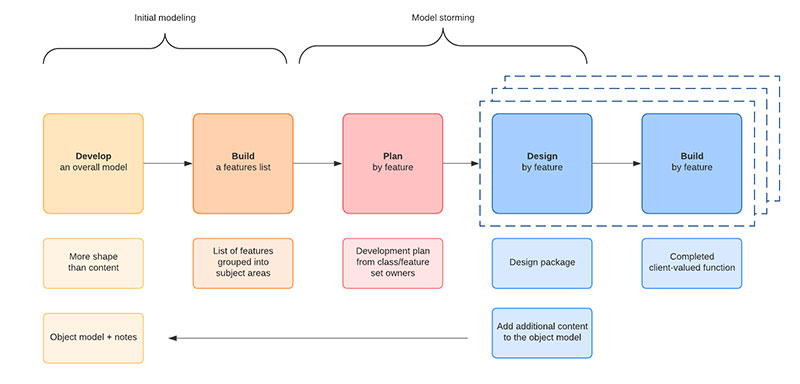
Image source: lucidchart.com
Feature Driven Development, or FDD is a software development methodology based on Agile. Its goal is simple, to prevent confusion that leads to costly rework.
FDD is sometimes mistaken as focusing on each of the software features. It is not.
To keep clients satisfied, developers calculate what features they can create. They break complex requests into smaller feature sets.
Then they put together a plan for how to reach each goal on time.
For frequent and efficient production of tangible software, FDD has five steps. The first step is to develop an overall model.
Next, build a feature list and then plan by each feature. The final two steps—design by feature and build by feature—will take up the majority of the effort.
At each step, the methodology encourages status reporting. This helps to track progress, results, and possible errors.
Application
This is an iterative methodology for software development. It aims to serve lots of teams working on a project based on object-oriented technology.
It is a good model for companies that are passing from a phase-based method to an iterative approach.
Pros
- Breaks down complicated tasks into smaller activities, which fuels efficiency.
- Based on predefined standards and best practices, which leads to predictable success.
- With this model, progress tracking of the project happens by a feature that is a focused approach.
- It allows multiple teams to work simultaneously. Which, in turn, saves time.
- FDD helps to move larger size projects and obtain repeatable success.
Cons
- The rigid structure of FDD makes it less desirable to teams who balance project-driven and break-fix types of work.
- Not an ideal methodology for smaller projects. So it is not good for an individual software developer.
- It places a high dependency on the main developer. That person must be able to act as coordinator, lead designer, and mentor.
- It can sometimes deviate from delivering value to the end-users. This is because the model is driven by activities.
We can help you turn your idea into reality, take over your existing project, or extend your current development team.
Schedule a free consultation at hello@tms-outsource.com, or fill out the form and we will follow up with you shortly.
DevOps Development Methodology
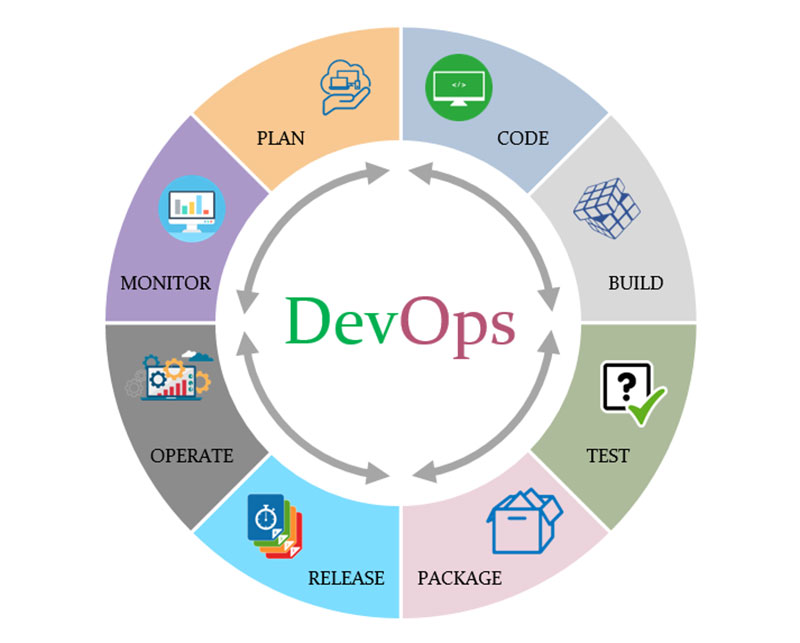
Image source: medium.com
DevOps is a popular term gaining a lot of attention. This is because of the unconditional benefits it offers to its customers.
The siloed process of Development and Operations is not the same as the inception of DevOps.
DevOps is not only a methodology for development. Rather, it is a series of activities that sustain an organizational culture.
The deployment of DevOps focuses on operational reform. This strengthens coordination between the divisions responsible for the development life cycle.
Such divisions include development, quality assurance, and operations.
Development and operational teams can work on things at the same time. This is thanks to the continuous integration and continuous delivery model.
They can perform everything, from development, quality assurance, and security, to other operations.
Application
DevOps may be particularly appropriate for founders of a technology startup. It can provide them with a quicker way to build apps.
It is also useful for project managers who need a more effective series of program testing procedures.
Pros
- A significant reduction in time to market and improved customer satisfaction.
- Simultaneous multiple ongoing processes. This makes the process faster and easier for businesses to process on time.
- With increasing changes in the product and infrastructure, the developed products are robust and secure.
- This is a collaborative platform pillared on strong parameters of accountability and ownership.
Cons
- Some customers don’t want continuous updates to their systems.
- Some industries have strict regulations. These require extensive testing before a project can move to the operations phase.
- If different departments use different environments, undetected issues can slip into production.
- Some quality attributes require human interaction, which slows down the delivery pipeline.
- Speed and security are not always achieved using DevOps.
Scrum Development Methodology
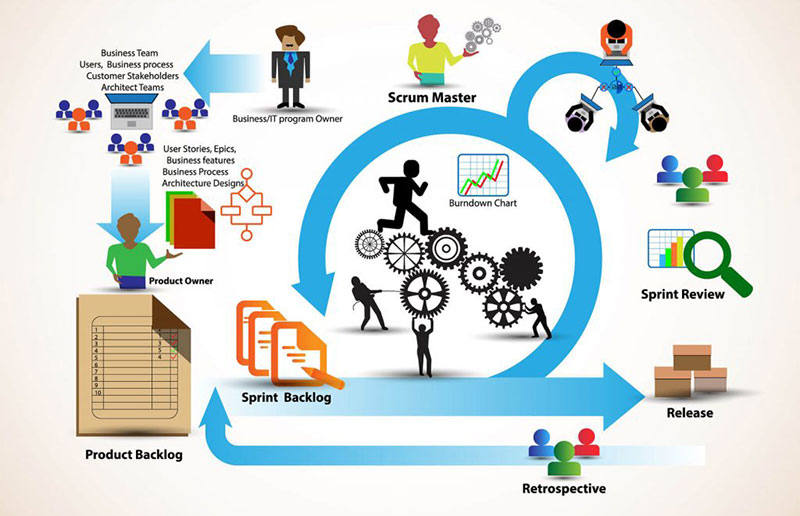
Image source: digite.com
The Scrum development methodology is useful in almost all project forms. As a phase of software development, it starts with a brief plan for each sprint.
Regular scrum meetings follow that demonstrate the success of the project. It concludes with a final analysis.
Team members break down end goals into smaller goals at the beginning of the lifecycle. They work through them using fixed-length iterations, or sprints.
In each sprint (which usually lasts two weeks), they build software and showcase it often.
It is a perfect approach because it is easy to track and progress projects.
Application
Scum is the go-to methodology if you have a project with vague requirements. The series of iterations help to generate the required software.
Pros
- Short iterations allow quick resolutions to problems.
- Scrum mixes the structure and discipline of more traditional software development methodologies with the flexibility and iterative practices of modern Agile.
- Decision-making lies in the hands of the team.
- Business requirement document is considered insignificant
- Scrum is economical and effective.
Cons
- There is no definite end date. So stakeholders may be tempted to keep demanding new functionality.
- It can lead to an inaccurate estimation of project costs and time. Thus, the development model suffers.
- It is good for small, fast-moving projects, but is not suitable for larger projects.
- All team members must be equally skilled and committed for Scrum to work.
- This methodology needs experienced team members.
- Project quality management is hard to implement and quantify. For this reason, the test team should conduct regression testing after each sprint.
Rapid Application Development
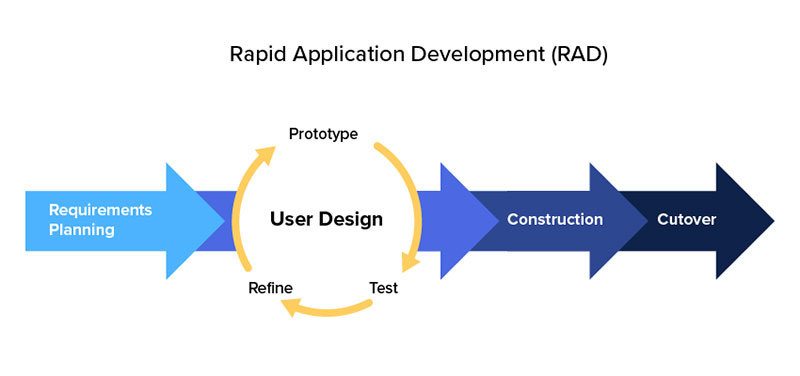
Image source: kissflow.com
The RAD approach came out of the need to deliver applications in a very short amount of time. In a nutshell, it’s a high-speed adaptation of the Waterfall method.
It achieves rapid development by using component-based construction.
The Rapid Application Development method contains four phases. These are:
- Requirements planning
- User design
- Construction
- Cutover
Phases 2 and 3 repeat until the user confirms that the product meets all requirements.
This methodology aims to improve the workability of the whole software or web application project. for highlighting the participation of an active user.
Application
For the best results, ensure to have a team of experienced developers. It also requires customers who are equally involved in the project.
Communication is key to realizing projects with the RAD method. Invest in RAD tools like low-code/no-code applications to speed up the development.
Pros
- As a result of prototyping in nature, there is less possibility of defects.
- Each phase in RAD delivers the highest priority functionality to the client.
- Risks reduction through regular customer feedback.
- Makes the entire development process effortless.
- Assists clients in taking quick reviews.
- Encourages feedback from customers for improvement.
Cons
- It only works on systems that can be modularized.
- Progress and problems are hard to track as there is no documentation.
- Dependent on the team for performance.
- Requires very skilled personnel to handle complexities.
- Not applicable for small budget projects.
Extreme Programming (XP)
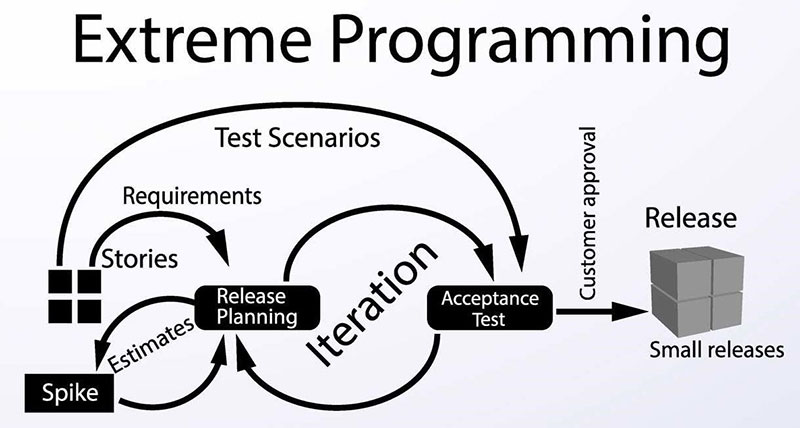
Image source: digite.com
With Extreme Programming, customer involvement in the software building process is high. This agile software engineering methodology is presently known as XP methodology.
In general, XP follows a set of values, rather than steps. These include:
- simplicity (develop what is required, nothing more)
- communication (teams must collaborate and work together on every piece of the software)
- consistent feedback
- respect
Application
Its prime use is for crafting software within a very unbalanced atmosphere.
The main goal of the XP model is to lower the cost of software requirements. It is quite common for the cost of changes at later stages in the project are very high.
Pros
- It focuses on customer involvement
- Establishes rational plans and schedules
- Developers have an exceptional commitment to the project
- Equipped with modernistic methods for quality software
- Allows software development companies to save on costs and time for project realization.
- This model is consistent with most modern development methods. So, developers are able to produce quality software.
Cons
- Effectiveness depends on the people involved
- Requires frequent meetings for development raising total costs
- Necessitates excessive development changes
- Exact possibilities and future outcomes are unknown
- Some specialists say that it is more focused on the code rather than on design.
Lean Development Methodology
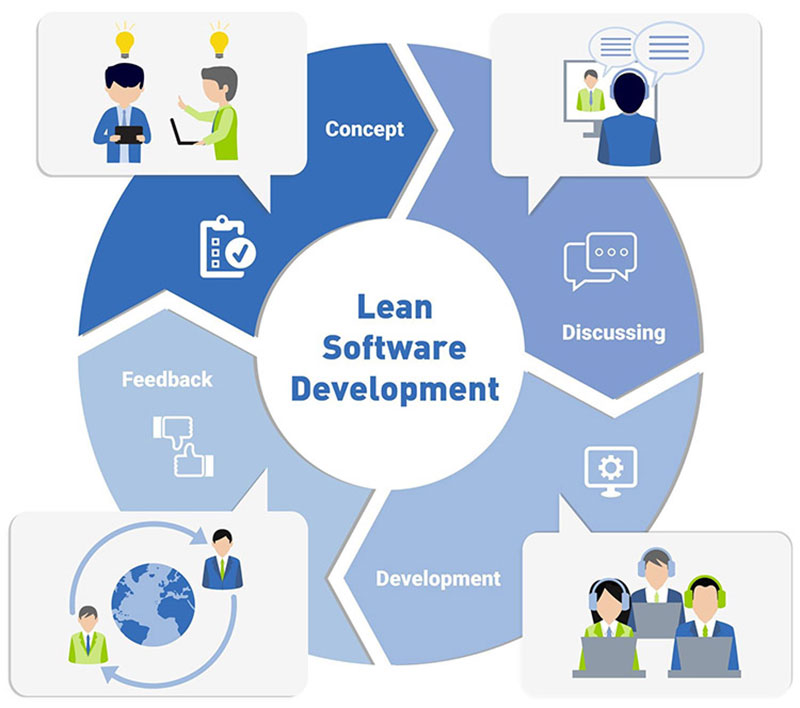
Image source: lvivity.com
The Lean methodology focuses on the development of low-budget software that is change-tolerant.
It maximizes resources by developing software with one-third the funds, human efforts, and production time. The workflow of Lean is minimal, and it cuts all forms of excesses such as meetings, documentation, and so on.
Lean development is born out of the Lean manufacturing principles of Toyota. Lean philosophies, practices, and tools help to innovate at scale.
The basic principles of Lean are:
- optimize the whole
- eliminate waste
- build quality in
- create knowledge
- defer commitment
- deliver fast
- respect people
These principles can guide decision-making across the organization. It helps to unearth potential issues and maintain a healthy organizational culture.
Application
Lean development is ideal for small projects with tight budgets. Minimizing waste and increasing efficiency allows small teams to achieve tremendous results.
Across industries, the Lean model reduces development costs and improves quality. It also increases productivity and improves customer satisfaction.
Pros
- The early elimination of waste speeds up the development process and reduces costs.
- It allows the team to speed up the development. Most projects complete in short time frames, beating deadlines.
- The Lean methodology empowers the development team. It motivates them to build acute decision-making abilities.
- Delivering a high-quality product on time leads to increased customer satisfaction.
- Increased motivation amongst team members.
Cons
- The method is team-dependent. So it’s essential to put together an excellent team with exceptional skill sets.
- Lean development requires detailed documentation.
- To benefit time and budget, all decisions must be accurate and final.
- To keep the project focused on the plan, there is a restriction on flexibility. This avoids unnecessary deviation and time loss.
Looking for a development partner?
If you’re looking for a technology partner, development team augmentation, or just a company for your software&app development initiatives, consider TMS.
TMS is a software and digital company in Belgrade, Serbia. We develop innovative and modern software.
A few examples include premium booking software Trafft, MedTech apps like MR Prepare, or MarTech/AdTech apps like the Advise Media Suite, among other great software examples.
Check out our services and also some of the work we’ve done for our clients. Who knows, maybe we’ll form a successful relationship.
Schedule a free consultation at hello@tms-outsource.com, or fill out the form and we will follow up with you shortly.
Conclusion on the software development methodologies you could use
Software development methods are a vital part of any development project.
This article considered eight of the best. But there are several other methods to consider.
For instance, Dynamic Systems Model, Prototype Model, and Object-Oriented Development (OOD). Each one has its own strengths and weaknesses and works well in different situations.
From industry experience, software development methodologies are more functional with certain project types. Different complexities demand different experts and levels of experience in the method of choice.
It is beneficial for software developers to know about these different methodologies. Thus they can select the right one for their software development projects.
If you enjoyed reading this article on software development methodologies, you should check out this one about software development outsourcing trends.
We also wrote about a few related subjects like lean software development, offshore software development, lean software development principles, how to hire a web development team, software development budget, business pivot examples, financial projections for startups, financial software development companies, IT outsourcing failures, and risk management processes.

